Wang, Y., Z.-Z. Hu, and F. Yan (2017), Spatiotemporal variations of differences between surface air and ground temperatures in China, J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 122, 7990–7999, doi:10.1002/2016JD026110
- They analyzed the differences between soil temperature and air temperature across China by using ground-based observations.
- They also compared the trends of air and soil temperature.
They indicated:
“The interdecadal variations of the tendencies of GST and SAT appear associated with the increase of snow depth in northern China (north of 40°N) in winter in recent decades, especially in northern Xinjiang, northern Inner Mongolia, and most parts of Northeast China.”
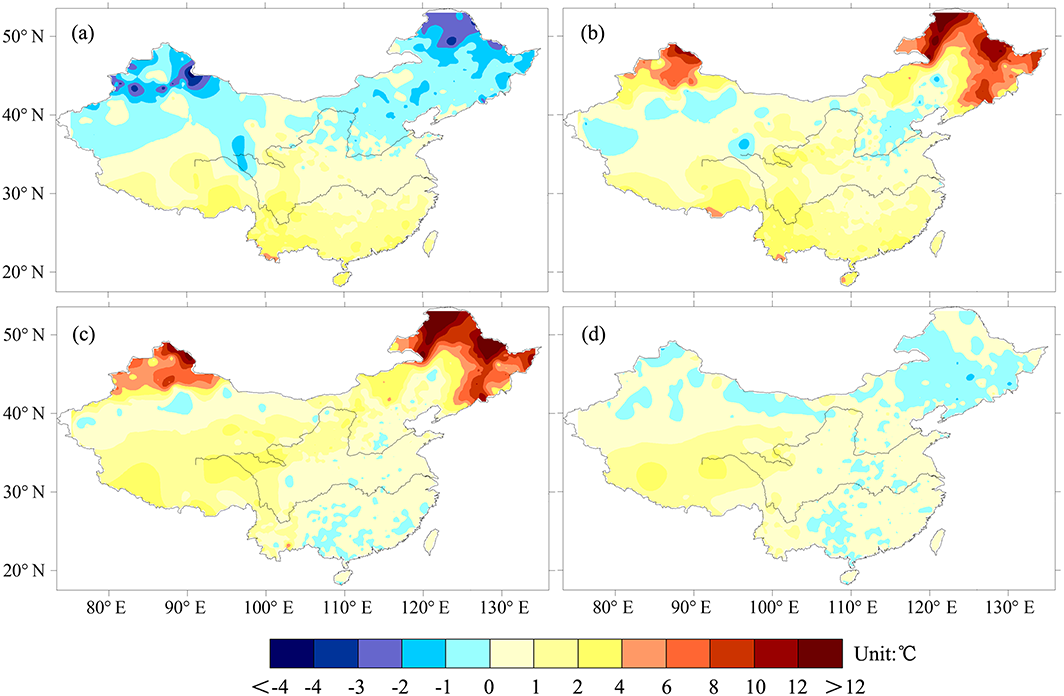
Fig.4 (a) Mean difference of GST-SAT over 1970–2004; (b) mean difference of GST-SAT over 2005–2015; (c) mean difference of GST between 2005–2015 and 1970–2004; (d) mean difference of SAT between 2005–2015 and 1970–2004.
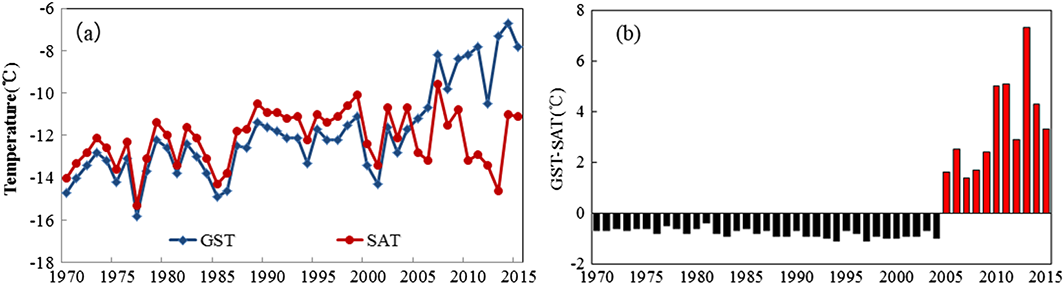
Fig.5 (a) Variations of GST and SAT and (b) difference of GST-SAT in northern China in winter over 1970–2015.

Fig.6 Spatial distributions of winter snow depth in China: (a) mean over 1970–2004, (b) mean over 2005–2015, and (c) difference between 2005–2015 and 1970–2004.
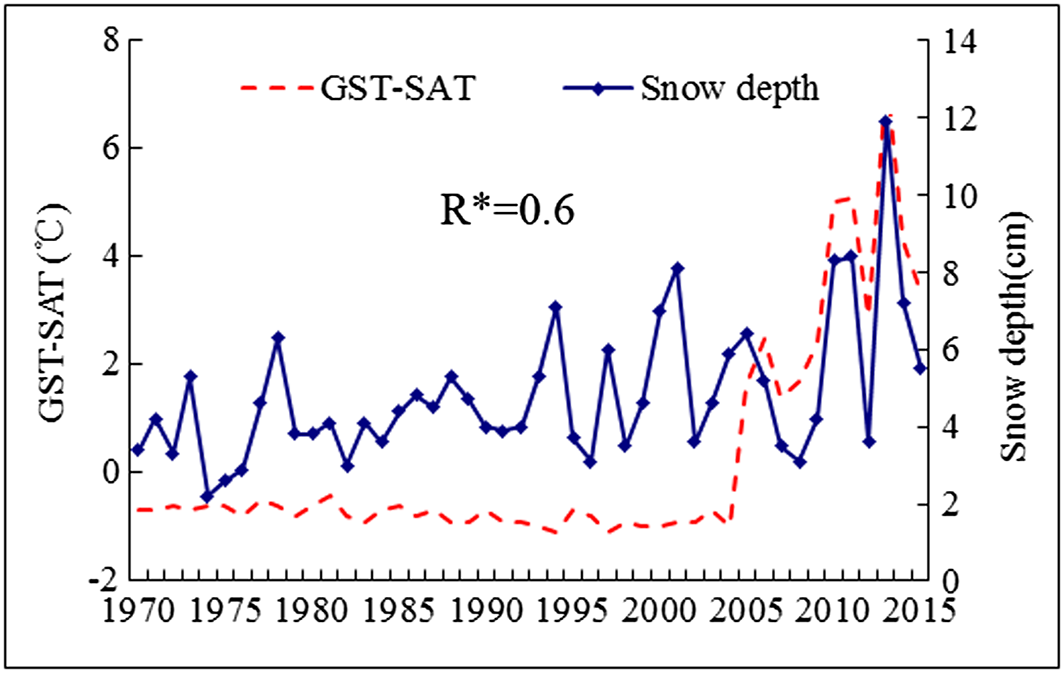
Fig.7 Variations of differences of GST-SAT and snow depth averaged in northern China (north of 40°N) in winter over 1970–2015.